Jeans Mass Eqiatopn - Pemersatu Bangsa Twitter Viral Video Museum : Pemersatu ... - Imagine this cloud is perturbed to initiate an isothermal collapse, e.g., with the density increasing like po 1/3 as the radius, r, decreases.. Where k is the boltzmann constant, t the temperature, r the radius of the cloud, g the gravitational constant, and m the average mass of a gas particle. We did not find results for: The dynamics of gas in the cloud is controlled by two uid equations: This gives a dispersion relation that is slightly different from equation (1.184) but the jeans mass remains unchanged. Then calculate the jeans mass of a typical molecular cloud with a temperature of 10 degrees k, a molecular hydrogen number density of 1010, and a corresponding density of 2mh nh2.
Taking the cloud to be spherical, the sphere gravitational potential energy is u = {3gm^2\over 5r}, where g is the gravitational constant, m. Mass problem became part of the larger dark matter problem that we first encountered within the milky way. I don't really know where to start. =,where is the spectral radiance, the power emitted per unit emitting area, per steradian, per unit wavelength; The jeans equations application of jeans equations the virial theorem collisionless systems introduction 2 stars almost never collide physically.

M j = (π/6) * ρ *λ j 3 where, m j = jeans mass π = 3.14 ρ = cloud mass density λ j = jeans length.
A cloud wtith radius r, mass m, and temperature t will collapse to form a star if the total energy of the cloud is <0, i.e, if the (absolute value) of the potential energy exceeds the thermal energy of the cloud: He was able to show that, under appropriate conditions, a cloud, or part of one, would become unstable and begin to collapse when it lacked sufficient gaseous pressure support to balance the force of gravity. Equations (1) and (2) represent 4 equations (1 scalar, 1 vector) in 5 unknowns (ˆ, p, and v). It is given by m j = 3ktr / 2gm. These are the seeds that evolve (gravitational collapse) to form the structured distribution of galaxies we see around us today: Distance to nearest star in a globular cluster is d ˘ 10 (106) 1 3 ˘0:1 pc ˘3 1015 m >>r ˘109 m. Check spelling or type a new query. This mass is known as the jean's mass, after the british physicist sir james jeans who first derived it. Nothing smaller than the whole system can be unstable to gravitational collapse. In this paper the formula is derived by studying small perturbations of the density and velocity in an expanding newtonian world. This problem sheet draws on information. In which is the standard jeans mass given by. Plugging these numbers into the collapse criterion equation and doing some math, we get the condition for collapse:
Then calculate the jeans mass of a typical molecular cloud with a temperature of 10 degrees k, a molecular hydrogen number density of 1010, and a corresponding density of 2mh nh2. This can reduce the flux by a factor of two in some cases. Imagine this cloud is perturbed to initiate an isothermal collapse, e.g., with the density increasing like po 1/3 as the radius, r, decreases. Jeans radius for cloud collapse. N is total number of particles in cloud.

I don't really know where to start.
R ˝d ˝r t this means that we can mentally smooth out the stars into a mean density ˆand use Assuming an isothermal (constant temperature) and. We did not find results for: M= (v^4)/ ( (p^.5) (g^1.5)) where v is the isothermal sound speed, and p is the pressure associated with the density ρ and temperature t. •release of egrav tends to increase internal temperature but also excites h2 and other molecules into excited rotational levels. M j = (π/6) * ρ *λ j 3 where, m j = jeans mass π = 3.14 ρ = cloud mass density λ j = jeans length. This is an online simple calculator which is used to calculate the jeans mass of the star formation using cloud mass density and jeans length. We need another equation to nd a solution. A more careful derivation from treating small perturbations to the equations of hydrostatic equilibrium (found here) produces a jeans length of times the jeans radius i derived above. Call this number the jean's mass, then we can say the cloud will collapse if its mass is bigger than the jean's mass. For wavelength , it is: This can reduce the flux by a factor of two in some cases. Voids, walls, filaments, clusters, galaxies, … !
These are the seeds that evolve (gravitational collapse) to form the structured distribution of galaxies we see around us today: The jeans mass is named after the british physicist sir james jeans, who considered the process of gravitational collapse within a gaseous cloud. Voids, walls, filaments, clusters, galaxies, … ! This is an online simple calculator which is used to calculate the jeans mass of the star formation using cloud mass density and jeans length. Nothing smaller than the whole system can be unstable to gravitational collapse.
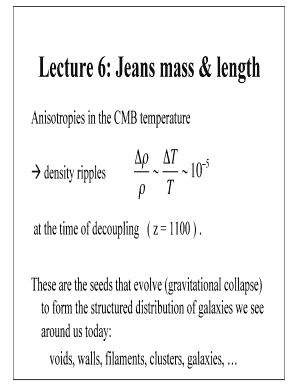
=,where is the spectral radiance, the power emitted per unit emitting area, per steradian, per unit wavelength;
This gives a dispersion relation that is slightly different from equation (1.184) but the jeans mass remains unchanged. He was able to show that, under appropriate conditions, a cloud, or part of one, would become unstable and begin to collapse when it lacked sufficient gaseous pressure support to balance the force of gravity. Maybe you would like to learn more about one of these? 4) a spherical cloud at the jeans mass will roughly satisfy the hydrostatic equilibrium equation, where the outward pressure force maintained by a pressure gradient roughly balances the inward force of gravity. In this paper the formula is derived by studying small perturbations of the density and velocity in an expanding newtonian world. I need to show that the critical (jeans') mass for a hydrogen cloud of uniform density to begin gravitational collapse can be expressed as: Jeans mass * this worksheet provides a derivation of the jeans mass formula and concludes with a problem making use of the formula. It was originally obtained for a static mass of uniform density, and the proof is questionable. For wavelength , it is: With the deflnition of the isothermal sound speed and the equation of state of an ideal gas cs = ˆ p0 ‰0!1=2 = ˆ k „mu t0!1=2 (19) where k is the boltzmann constant, „ the mean molecular weight and mu = 1:66¢10¡27 kg the atomic mass unit, we obtain mj = ‰ 0 ˆ. Jeans mass & length anisotropies in the cmb temperature density ripples at the time of decoupling ( z = 1100 ). We did not find results for: Equations (1) and (2) represent 4 equations (1 scalar, 1 vector) in 5 unknowns (ˆ, p, and v).